What is Tick-borne Encephalitis
Tick-borne Encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection that affects the central nervous system and is found in various regions, including eastern, northern, and central Europe, as well as eastern Russia, East Asia, China, and Japan. The TBE virus is primarily transmitted through the bites of infected ticks. These ticks commonly inhabit forests, grasslands, and woodlands, thriving in environments with dense vegetation and high humidity. TBE is not transmitted from person to person, as there is no human-to-human transmission of the virus. The primary mode of infection is through direct contact with ticks during outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or working in endemic areas. In some cases, the virus can also be transmitted through the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products from infected animals.
How to prevent Tick-borne Encephalitis
Preventing TBE involves a combination of vaccination, tick-avoidance strategies, and prompt tick removal. Vaccination is highly effective and recommended for people living in or traveling to areas where TBE is endemic. To avoid tick bites, individuals should wear long-sleeved clothing, tuck trousers into socks, and use insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin when spending time in wooded or grassy areas. After outdoor activities, it is important to conduct thorough tick checks on the body and promptly and properly remove any attached ticks with tweezers. These measures significantly reduce the risk of contracting TBE.
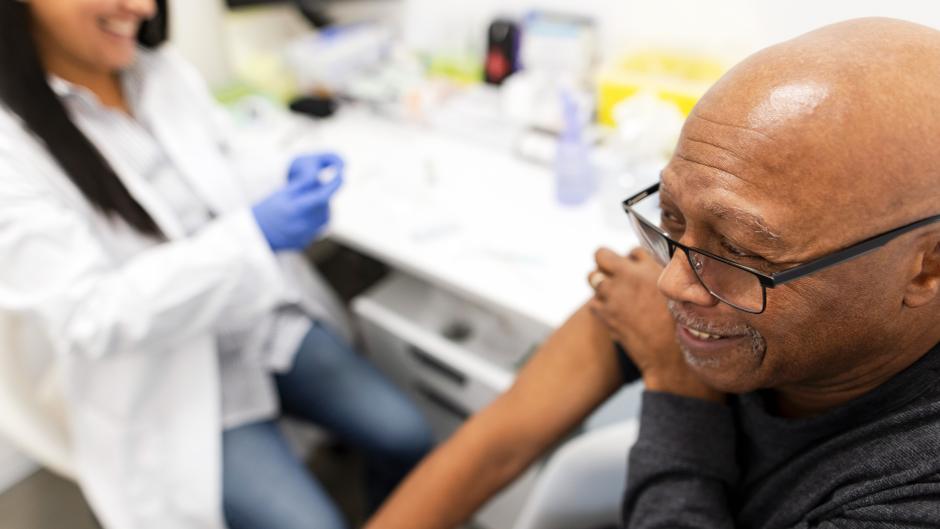
Tick-borne Encephalitis vaccinations
£60 per dose